Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) in the US: Can It Cut Congestion?
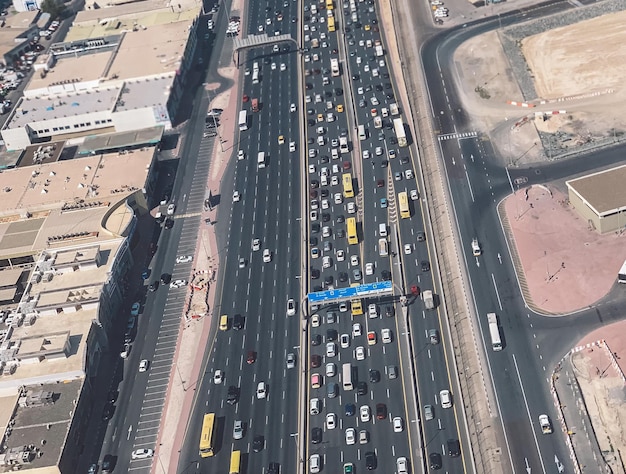

Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) in the US could potentially reduce traffic congestion by 20% through integrated platforms that streamline transportation options, offering a user-centric approach to urban mobility and decreasing reliance on private vehicles.
Is Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) in the US: Are Integrated Platforms the Key to Reducing Traffic Congestion by 20%? a feasible solution to alleviate the growing traffic congestion problems plaguing American cities? Integrated MaaS platforms offer a user-friendly approach to transportation, potentially shifting commuters away from private vehicles.
The Promise of Mobility-as-a-Service in the US
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) is gaining traction as a potential game-changer in urban transportation. The concept centers around integrating various transport modes—public transit, ride-sharing, bike rentals, and more—into a single, user-friendly platform.
Could this integrated approach be the key to significantly reducing traffic congestion in the US? Let’s delve into the potential of MaaS to transform how Americans move.
What Exactly is Mobility-as-a-Service?
At its core, MaaS is about providing seamless, on-demand access to a range of transportation options. Instead of relying solely on personal car ownership, users can subscribe to a MaaS platform and choose the most efficient and cost-effective mode for each journey.
This can range from a quick bus ride to a combination of train and bike-sharing, all managed through a single app.
- Reduces reliance on private vehicles.
- Offers personalized transportation plans.
- Provides real-time information and booking.
- Can integrate with existing transportation infrastructure.
MaaS aims to make transportation more convenient, affordable, and sustainable. By offering a viable alternative to car ownership, it has the potential to ease congestion and improve air quality in urban areas.
Current Traffic Congestion Challenges in US Cities
Traffic congestion is a costly and frustrating reality for millions of Americans. It not only wastes time and fuel but also contributes to air pollution and economic losses. Understanding the scope of the problem is crucial to assessing the potential impact of MaaS.
How severe is the current traffic situation in US cities, and what are the key contributors to this congestion?
The Economic and Environmental Costs of Congestion
The consequences of traffic congestion extend far beyond mere inconvenience. Studies have shown that it imposes significant economic and environmental burdens on individuals, businesses, and society as a whole.
- Lost productivity and wasted fuel cost billions annually.
- Increased vehicle emissions contribute to air pollution and climate change.
- Traffic delays negatively impact supply chains and logistics.
- Commuting stress affects mental and physical health.
The widespread adoption of MaaS could help alleviate some of these costs by encouraging a shift towards more efficient and sustainable modes of transportation.
Current traffic congestion in major US cities poses a significant economic and environmental challenge, costing billions in lost productivity and contributing to increased pollution levels. MaaS offers a potential pathway to alleviate these issues.
How MaaS Platforms Aim to Reduce Congestion by 20%
The ambitious goal of reducing traffic congestion by 20% through MaaS hinges on several key factors. Integrated platforms can influence travel behavior and optimize the use of existing transportation infrastructure.
What strategies do MaaS platforms employ to achieve this significant reduction in traffic density?
MaaS platforms can significantly impact urban congestion through several mechanisms. By integrating transportation options and providing real-time data, these platforms encourage users to make more informed travel decisions.
Incentivizing Public Transit and Shared Mobility
A key aspect of MaaS is to incentivize the use of public transit and shared mobility services. This can be achieved through discounted fares, bundled packages, and convenient booking options.
By making these alternatives more attractive than driving a private vehicle, MaaS platforms can encourage commuters to leave their cars at home, resulting in reduced traffic on the roads.
- Promoting public transit through integrated ticketing.
- Offering incentives for using shared mobility services.
- Providing real-time information on route optimization.
- Encouraging multi-modal transportation options.
By offering a more appealing and convenient user experience, MaaS platforms aim to shift travel behavior away from private vehicle use and towards more sustainable options.
MaaS platforms aim to reduce congestion by incentivizing public transit and shared mobility, offering attractive alternatives to private car use through integrated ticketing, real-time information, and optimized route planning.

Examples of Successful MaaS Implementations Globally
While MaaS is still in its early stages of development in the US, several successful implementations around the world offer valuable insights and lessons. These examples demonstrate the potential benefits and challenges of deploying MaaS platforms in different urban contexts.
What can the US learn from these international examples to ensure successful MaaS deployments?
Helsinki: A Pioneer in Mobility-as-a-Service
Helsinki, Finland, is widely recognized as a pioneer in MaaS implementations. Its Whim app integrates various transportation options, allowing users to plan and pay for journeys using a single platform.
The Whim app has been successful in attracting a significant number of users and reducing car ownership in Helsinki. It serves as a model for other cities looking to implement similar MaaS platforms.
- Reduced car ownership rates.
- Increased use of public transit.
- Improved accessibility for residents.
The success of Helsinki’s Whim app demonstrates the potential for MaaS to transform urban transportation. By offering a convenient and affordable alternative to private car ownership, MaaS can contribute to a more sustainable and livable city.
Global examples, like Helsinki’s Whim app, demonstrate the potential of MaaS to reduce car ownership and increase public transit usage through integrated platforms, offering valuable lessons for US implementations.
Challenges and Obstacles to MaaS Adoption in the US
Despite its promises, the widespread adoption of MaaS in the US faces several challenges and obstacles. These include regulatory hurdles, technological integration issues, and public acceptance concerns.
What are the key challenges that need to be addressed to ensure the successful implementation of MaaS in the US?
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
MaaS platforms rely on collecting and analyzing vast amounts of user data to optimize transportation services. This raises legitimate concerns about data privacy and security.
Users need to be confident that their personal information is protected and that their travel data is not being misused. Addressing these concerns is crucial to building trust and encouraging widespread MaaS adoption.
- Ensuring data privacy compliance.
- Implementing robust security measures.
- Providing transparency on data usage.
Overcoming these obstacles and building trust among users is essential for the successful deployment of MaaS in the US. Collaboration, innovation, and a user-centric approach will be key to unlocking the full potential of MaaS as a solution to urban traffic congestion.
MaaS adoption in the US faces challenges, particularly around data privacy and security, requiring robust measures and transparent data usage policies to build user trust.
Policy and Regulatory Considerations for MaaS in the US
The deployment of MaaS platforms in the US requires careful consideration of policy and regulatory frameworks. Existing transportation regulations may need to be adapted to accommodate new mobility services and ensure fair competition.
What role should policymakers play in shaping the future of MaaS in the US?
Collaboration Between Public and Private Sectors
Successful MaaS implementations often involve close collaboration between public and private sector stakeholders. This collaboration is essential for aligning MaaS platforms with public transportation goals and ensuring equitable access for all users.
Public agencies can provide valuable data, infrastructure, and regulatory support, while private companies can bring innovation, technology, and customer service expertise.
- Establishing clear regulatory guidelines.
- Promoting open data sharing and interoperability.
- Addressing equity gaps in transportation access.
A well-defined policy and regulatory framework is essential for fostering a thriving MaaS ecosystem in the US. By working together, public and private sector stakeholders can create a transportation system that is more efficient, sustainable, and equitable.
Effective MaaS implementation in the US requires strong collaboration between public and private sectors to establish clear regulations, promote data sharing, and address equity gaps in transportation access.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🚗 MaaS Definition | Integrated transport via single platform, reducing car reliance. |
| 🚦 Congestion Costs | Economic and environmental losses due to traffic inefficiencies. |
| 🌍 Global Examples | Helsinki’s Whim app shows MaaS success in cutting car ownership. |
| 🔒 Data Privacy | Important to secure user data and build trust in MaaS platforms. |
[title da seção FAQ em en-US]
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
▼
MaaS integrates various transport options into one platform, offering users seamless access to different modes of transportation. It’s designed to be a user-centric approach, promoting efficient travel choices.
▼
By providing convenient access to public transit and shared mobility, MaaS incentivizes users to reduce their reliance on private cars, decreasing traffic volume and promoting sustainable transportation.
▼
Helsinki’s Whim app is a prime example, integrating various transport modes into a single platform. It has successfully reduced car ownership and increased public transit usage in the city.
▼
Challenges include regulatory hurdles, technological integration issues, and concerns about data privacy and security. Building trust and ensuring data protection are essential for successful MaaS adoption.
▼
Policies should promote collaboration between public and private sectors, ensuring equitable access and clear regulatory guidelines. This support is critical for fostering a thriving MaaS ecosystem.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) in the US: Are Integrated Platforms the Key to Reducing Traffic Congestion by 20%? holds significant potential for transforming urban mobility and alleviating traffic congestion. While challenges remain, successful implementations worldwide demonstrate the feasibility of MaaS. By embracing integrated platforms, fostering collaboration, and prioritizing user needs, the US can pave the way for a future where transportation is more efficient, sustainable, and equitable for all.





