EV Maintenance Landscape 2026: 7 Key Considerations & Solutions

Navigating the EV Maintenance Landscape in 2026 requires understanding evolving technologies, specialized training, and proactive battery management to ensure the longevity and efficiency of electric vehicles.
The automotive world is undergoing a profound transformation, with electric vehicles (EVs) at the forefront of this revolution. As we approach 2026, the complexity and sophistication of these machines continue to grow, presenting both opportunities and challenges for owners and service providers alike. Understanding the nuances of the EV Maintenance Landscape is no longer optional; it’s a critical component of sustainable mobility. This article delves into seven essential considerations, offering practical solutions to keep your electric vehicle running efficiently and reliably in the years to come.
The evolving nature of EV powertrains and components
Electric vehicle technology is advancing at an unprecedented pace, fundamentally altering the traditional maintenance paradigm. Unlike internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, EVs feature fewer moving parts, reducing the frequency of certain mechanical failures. However, this simplicity introduces new complexities, particularly concerning high-voltage systems and sophisticated software. The shift from mechanical to electrical and software-driven systems necessitates a complete re-evaluation of maintenance practices.
The core of an EV’s powertrain consists of the electric motor, power electronics, and the high-voltage battery. These components are designed for durability but require specialized knowledge for inspection and repair. Traditional mechanics often lack the training and equipment to safely and effectively service these systems, creating a demand for a new generation of EV-certified technicians. Furthermore, the integration of advanced sensors and control units means that diagnostic procedures are increasingly reliant on software tools and manufacturer-specific protocols.
High-voltage battery management
The battery pack is the most critical and often the most expensive component of an EV. Proper care and monitoring are paramount for its longevity and performance. Unlike conventional car batteries, EV batteries are complex systems with sophisticated thermal management and cell balancing features.
- Regular diagnostic checks: Specialized tools are needed to monitor cell health, temperature, and overall battery performance.
- Thermal management system maintenance: Ensuring the cooling or heating system for the battery is functioning optimally is crucial to prevent degradation.
- Software updates: Battery management system (BMS) software updates can improve efficiency, range, and longevity.
Understanding the intricacies of battery health and proactively addressing potential issues can significantly extend the life of an EV. This involves not only routine checks but also adopting smart charging habits and avoiding extreme temperatures when possible. The continued evolution of battery chemistry and architecture further emphasizes the need for up-to-date knowledge and specialized servicing.
Impact of software and over-the-air updates
In 2026, software is not just an add-on; it’s integral to the very operation and maintenance of electric vehicles. Over-the-air (OTA) updates have become a standard feature, allowing manufacturers to remotely enhance vehicle performance, introduce new functionalities, and, critically, address potential issues without requiring a visit to a service center. This paradigm shift has profound implications for how maintenance is perceived and executed.
OTA updates can improve everything from powertrain efficiency and battery management to infotainment systems and advanced driver-assistance features. For owners, this means their vehicle can continuously improve over time, potentially avoiding costly recalls or inconvenient service appointments for software-related fixes. However, it also means that diagnostic tools and technician training must keep pace with these frequent software revisions, ensuring compatibility and understanding of new system behaviors.
Diagnostic capabilities and challenges
The reliance on software extends to diagnostics. Modern EVs generate vast amounts of data, which, when properly analyzed, can provide deep insights into the vehicle’s health. Specialized diagnostic software, often proprietary to manufacturers, is essential for interpreting error codes, monitoring sensor data, and performing calibration procedures. This creates a barrier for independent repair shops that may not have access to the same tools and information as authorized dealerships.
- Proprietary tools: Access to manufacturer-specific diagnostic equipment and software is often limited.
- Data interpretation: Technicians need advanced training to understand complex data streams and identify root causes of issues.
- Cybersecurity concerns: OTA updates and connected vehicle systems introduce new cybersecurity risks that must be managed.
The challenge lies in ensuring that all service providers, including independent shops, have the necessary resources and training to effectively diagnose and repair software-driven issues. This requires ongoing collaboration between manufacturers, training institutions, and the aftermarket industry to disseminate knowledge and tools. The future of EV maintenance is undeniably intertwined with the ability to manage and leverage software effectively.
Specialized technician training and certification
The rapid proliferation of electric vehicles has created a significant skills gap in the automotive service industry. Servicing EVs, particularly their high-voltage systems, requires specialized knowledge and strict safety protocols that differ dramatically from those for ICE vehicles. By 2026, the demand for certified EV technicians will be more critical than ever, influencing everything from repair costs to vehicle downtime.
Technicians must be trained not only in electrical safety procedures but also in the intricacies of high-voltage battery systems, electric motors, power electronics, and thermal management. This training often involves understanding complex schematics, using specialized insulated tools, and adhering to strict lockout/tagout procedures to prevent accidental electrocution. Without this specialized expertise, both technicians and vehicle owners face significant risks.
Accreditation and ongoing education
Certification programs, often offered by manufacturers or industry organizations, are becoming the benchmark for qualified EV technicians. These programs ensure that individuals possess the theoretical knowledge and practical skills required to safely and effectively work on electric vehicles. However, given the fast pace of technological advancement, continuous learning is essential.
- Manufacturer-specific training: Many EV manufacturers offer their own training and certification paths for their specific vehicle platforms.
- Industry certifications: Organizations like ASE (Automotive Service Excellence) are developing certifications specifically for EV and hybrid vehicle maintenance.
- Safety protocols: Comprehensive training on high-voltage safety is non-negotiable for all EV service personnel.
The investment in technician training is not just about compliance; it’s about ensuring quality service, reducing repair times, and ultimately building consumer confidence in the EV ecosystem. As the EV fleet grows, a robust network of certified technicians will be crucial for supporting widespread adoption and maintaining vehicle reliability.
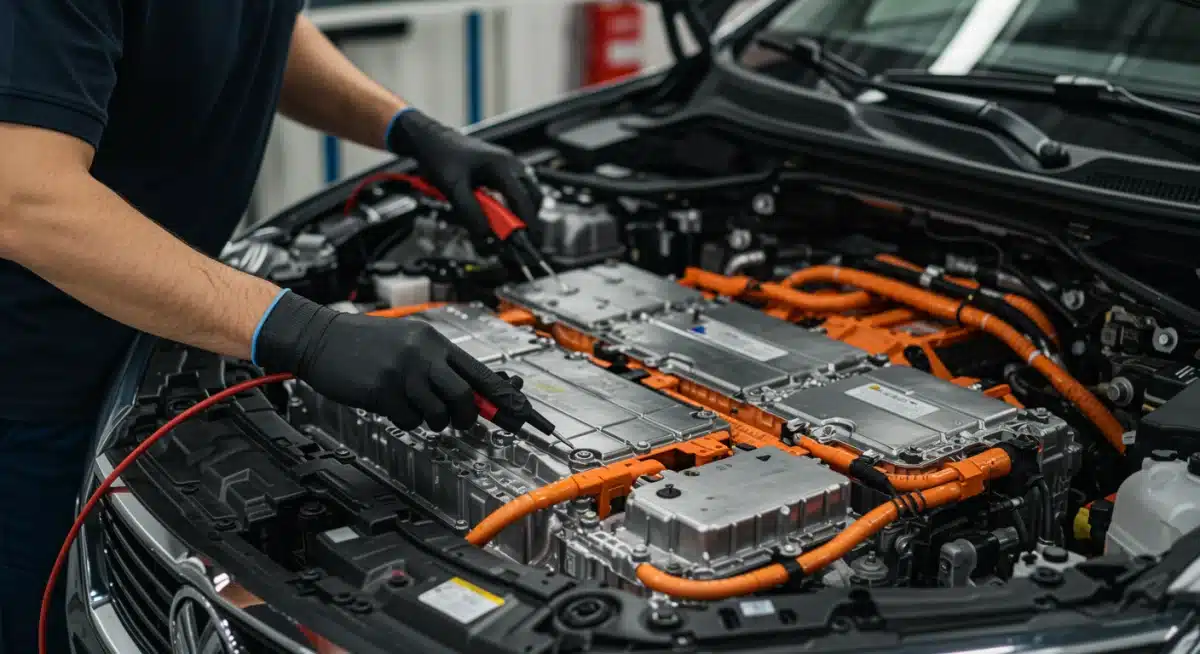

Infrastructure for charging and service
The growth of the EV market is inextricably linked to the development of robust charging and service infrastructure. While charging networks have seen significant expansion, the infrastructure for specialized EV maintenance and repair is still catching up. By 2026, a more comprehensive and accessible service network will be vital for supporting the increasing number of electric vehicles on the road, particularly in regions with high EV adoption.
Service centers need to be equipped with specific tools, such as insulated gloves, high-voltage multimeters, battery lifting equipment, and dedicated charging stations for diagnostic purposes. Furthermore, the physical layout of workshops may need to be adapted to safely accommodate high-voltage vehicles and their unique service requirements. This includes designated areas for battery repair and storage, as well as specialized fire suppression systems.
Expanding service networks
The geographic distribution of EV service centers is uneven, with a higher concentration in urban areas. As EVs become more prevalent in suburban and rural settings, the need for accessible service options will grow. This involves not only establishing new service locations but also retrofitting existing ones with the necessary equipment and trained personnel.
- Dedicated EV service bays: Workshops need specific areas designed for high-voltage work, ensuring safety and efficiency.
- Parts availability: A reliable supply chain for EV-specific components, including battery modules and power electronics, is crucial.
- Mobile service options: Some manufacturers are exploring mobile service units capable of performing minor repairs and diagnostics on-site.
Developing this infrastructure requires significant investment and strategic planning. It’s a collaborative effort involving vehicle manufacturers, government agencies, and independent service providers to ensure that EV owners have convenient and reliable access to maintenance and repair services, fostering greater confidence in electric mobility.
The role of predictive maintenance and AI
The future of EV maintenance in 2026 will be heavily influenced by advancements in predictive maintenance and artificial intelligence (AI). Leveraging real-time data from vehicle sensors and integrating AI-driven analytics can transform maintenance from a reactive process to a proactive one. This shift has the potential to significantly reduce unexpected breakdowns, optimize service schedules, and extend the lifespan of EV components.
Modern EVs are equipped with dozens, if not hundreds, of sensors that constantly monitor various aspects of the vehicle’s performance, from battery cell temperatures to motor efficiency. AI algorithms can analyze this vast amount of data to identify subtle patterns that indicate potential issues before they escalate into major problems. This allows for timely interventions, often through software updates or scheduled maintenance, minimizing downtime and repair costs.
Data-driven insights for owners and technicians
Predictive maintenance capabilities can provide valuable insights to both vehicle owners and service technicians. Owners might receive alerts about potential issues, along with recommendations for proactive service. Technicians, armed with detailed diagnostic data, can pinpoint problems more quickly and accurately, leading to more efficient repairs.
- Early fault detection: AI can identify anomalies in performance data that signal impending component failure.
- Optimized service intervals: Maintenance schedules can be tailored to the actual condition and usage patterns of the vehicle, rather than fixed mileage intervals.
- Enhanced safety: Proactive identification of potential issues can prevent safety-critical failures.
The integration of AI and predictive analytics in EV maintenance represents a significant leap forward. It moves beyond simple diagnostics to intelligent forecasting, ensuring that electric vehicles remain reliable and perform optimally throughout their operational life, paving the way for more efficient and sustainable transportation.
Cost considerations for EV maintenance
While electric vehicles are often lauded for their lower running costs compared to ICE vehicles, particularly regarding fuel and some routine maintenance items, it’s crucial to understand the evolving cost landscape for EV maintenance in 2026. The absence of oil changes, spark plug replacements, and complex exhaust systems reduces some expenses, but new cost factors emerge, primarily related to specialized components and labor.
The high-voltage battery pack, though designed for longevity, can be an extremely expensive component to replace if it fails outside of warranty. Similarly, electric motors and advanced power electronics, while reliable, can incur significant costs if repairs are needed due to their specialized nature and the expertise required. Labor costs for EV-specific repairs can also be higher due to the specialized training and equipment required for technicians.
Long-term value and preventative care
Despite these specific cost considerations, the overall cost of ownership for EVs often remains competitive, especially when considering fuel savings and potential government incentives. The key to managing maintenance costs effectively lies in preventative care and understanding warranty coverage.
- Battery warranty: Most EV manufacturers offer extensive warranties on their battery packs, typically 8 years or 100,000 miles.
- Brake longevity: Regenerative braking significantly reduces wear on traditional brake components, leading to longer intervals between replacements.
- Fewer fluids: EVs require fewer fluid changes (e.g., no engine oil), simplifying routine service.
Owners can mitigate potential high costs by adhering to manufacturer-recommended service schedules, promptly addressing any warning signs, and ensuring their vehicle is serviced by certified professionals. Focusing on proactive maintenance and leveraging warranty protections are essential strategies for cost-effective EV ownership in the long term.
Recycling and end-of-life considerations
As the electric vehicle fleet continues to grow, the question of what happens to EV components at the end of their useful life becomes increasingly important. By 2026, the focus on sustainability will extend beyond just vehicle operation to encompass the entire lifecycle, including responsible recycling and disposal of key components, particularly battery packs. This is not just an environmental concern but also an economic one, as valuable materials can be recovered.
EV batteries contain valuable materials such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese. Recovering these materials through efficient recycling processes reduces the need for virgin mining and minimizes environmental impact. However, the complexity of battery chemistry and structure presents significant challenges for cost-effective and environmentally sound recycling at scale. New technologies and processes are continually being developed to address these issues.
Circular economy for EV components
The concept of a circular economy, where materials are reused and recycled to minimize waste, is gaining traction in the EV industry. This includes not only battery recycling but also the potential for repurposing EV battery packs for second-life applications, such as stationary energy storage, before they are eventually recycled. This extends the economic value and environmental utility of these components.
- Battery recycling infrastructure: Investment in advanced battery recycling facilities is crucial for handling increasing volumes.
- Material recovery: Developing processes to efficiently extract valuable raw materials from spent batteries.
- Second-life applications: Exploring opportunities to repurpose EV batteries for other uses, like grid storage, after their automotive life.
Addressing end-of-life considerations for EVs is a critical aspect of ensuring their long-term sustainability. It requires innovation in recycling technologies, robust regulatory frameworks, and collaborative efforts across the industry to establish efficient and environmentally responsible pathways for battery disposal and material recovery, contributing to a truly green mobility future.
| Key Consideration | Practical Solution |
|---|---|
| EV Powertrain Evolution | Regular diagnostic checks and thermal management system maintenance for high-voltage batteries. |
| Software & OTA Updates | Ensure technicians have access to proprietary diagnostic tools and continuous training on new software. |
| Technician Training | Invest in manufacturer-specific and industry certifications, focusing on high-voltage safety. |
| Predictive Maintenance | Utilize AI-driven analytics for early fault detection and optimized, data-driven service intervals. |
Frequently Asked Questions about EV Maintenance
EVs require less routine maintenance due to fewer moving parts, eliminating oil changes and spark plug replacements. However, they demand specialized attention for high-voltage battery systems, electric motors, power electronics, and sophisticated software diagnostics, which differ significantly from traditional vehicle upkeep.
EV batteries typically don’t require routine maintenance beyond software updates and thermal system checks. They are designed for the life of the vehicle, often coming with 8-year/100,000-mile warranties. Replacement is rare and usually only necessary in cases of significant degradation or damage, which is often covered by warranty.
While routine EV maintenance costs are generally lower, major component replacements like the battery can be expensive if not covered by warranty. However, overall cost of ownership often favors EVs due to fuel savings and reduced wear on parts like brakes, making them competitive over the long term.
Software updates are crucial for EVs, enhancing performance, efficiency, and safety. Over-the-air (OTA) updates can address issues, improve battery management, and add new features, often eliminating the need for physical service visits. They are a fundamental part of keeping an EV optimized and up-to-date.
By 2026, finding qualified EV technicians will be easier, though specialized training remains key. Look for authorized dealerships, independent shops with EV certifications (like ASE’s EV/Hybrid specialty), or consult manufacturer websites for recommended service centers. Always verify a technician’s high-voltage safety training.
Conclusion
The year 2026 marks a pivotal point in the evolution of electric vehicles, and with it, the landscape of automotive maintenance. The transition from internal combustion engines to sophisticated electric powertrains demands a proactive and informed approach to vehicle care. From mastering the intricacies of high-voltage battery systems to embracing the power of over-the-air software updates and AI-driven predictive analytics, the future of EV maintenance is dynamic and exciting. Investing in specialized technician training, expanding robust service infrastructure, and understanding the evolving cost and end-of-life considerations are not just challenges but opportunities. By addressing these seven key considerations with practical solutions, we can ensure that electric vehicles continue to deliver on their promise of sustainable, efficient, and reliable transportation for years to come, fostering greater confidence and accelerating the global shift towards electric mobility.