Smart Waste Management: AI Cuts Landfill Waste by 30%

Smart Waste Management leverages AI-powered systems to optimize waste collection, sorting, and processing, aiming to reduce landfill waste by up to 30% through enhanced efficiency and resource recovery.
Is your city drowning in waste? Discover how Smart Waste Management, powered by AI, can drastically reduce landfill waste by 30%, creating a cleaner, more sustainable urban environment.
The Growing Problem of Landfill Waste
Landfills are a growing concern for cities worldwide. Space is running out, and the environmental impacts are significant, ranging from greenhouse gas emissions to soil and water contamination. Traditional waste management systems are struggling to keep up with the increasing volume and complexity of waste generated by urban populations.
Finding innovative solutions is now indispensable. The potential of AI in revolutionizing smart waste management is increasingly recognized as a means to minimize landfill waste and create a more sustainable future.
The Environmental Impact of Landfills
Landfills pose several environmental threats, including:
- Methane emissions: a potent greenhouse gas contributing to climate change.
- Leachate contamination: toxic liquids polluting soil and groundwater.
- Habitat destruction: impacting local ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Air pollution: caused by dust and other particulate matter released from landfills.
These factors call for smarter, more efficient waste management strategies.
The Limitations of Traditional Waste Management
Conventional waste management methods often fall short due to:
- Inefficient sorting processes: resulting in a high percentage of recyclable materials ending up in landfills.
- Suboptimal collection routes: leading to increased fuel consumption and emissions.
- Lack of real-time data: hindering effective monitoring and decision-making.
AI-powered systems provide solutions to these challenges by optimizing every aspect of the waste management process.

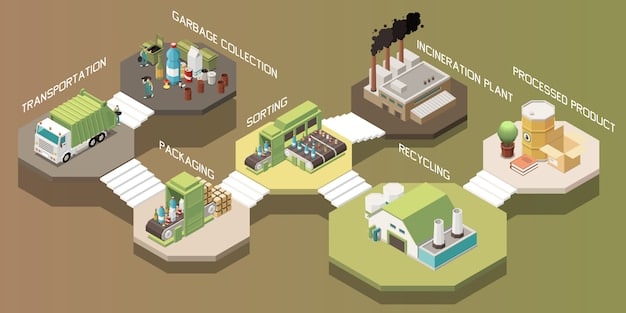
How AI is Transforming Waste Management
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming waste management by introducing automation, predictive analytics, and optimization across various stages. From collection and sorting to processing and disposal, AI algorithms are enhancing efficiency, minimizing waste, and maximizing resource recovery.
With real-time data analysis and machine learning, AI can tackle challenges traditional systems struggle with, paving the way for a more sustainable and streamlined waste management ecosystem.
AI-Powered Waste Sorting
AI significantly improves waste sorting accuracy and speed using:
- Computer vision: identifying different types of materials based on visual characteristics.
- Robotic arms: automating the sorting process with precision and efficiency.
- Machine learning: continuously improving sorting accuracy through data analysis.
These technologies reduce the amount of recyclable materials ending up in landfills.
Optimized Waste Collection Routes
AI algorithms optimize waste collection routes by considering factors such as:
- Real-time traffic data: avoiding congestion and minimizing travel time.
- Waste fill levels: prioritizing collection based on container capacity.
- Predictive analysis: forecasting waste generation patterns to optimize schedules.
The result is lower fuel consumption and reduced emissions from collection vehicles.
In conclusion, AI is proving to be an efficient tool in achieving a circular economy.
The Benefits of AI-Powered Smart Waste Management
Implementing AI-powered smart waste management systems offers several compelling advantages, including significant reductions in landfill waste, cost savings, enhanced operational efficiency, and improved environmental outcomes. Cities adopting these technologies are moving closer to sustainable waste management.
The ability of AI to optimize processes and make data-driven decisions makes it a key component in modern waste management strategies.
Cost Savings and Efficiency
Integrating AI in waste management leads to notable cost reductions through:
- Reduced labor costs: automating sorting and collection processes minimizes the need for manual labor.
- Lower fuel consumption: optimizing collection routes saves on fuel expenses.
- Increased recycling rates: generating revenue from recovered materials.
These efficiencies offer substantial financial benefits to municipalities and waste management companies.
Improved Environmental Impact
AI-driven waste management contributes to a healthier environment by:
- Reducing methane emissions: decreasing the amount of organic waste in landfills.
- Minimizing leachate contamination: diverting hazardous materials from landfills.
- Conserving natural resources: maximizing the recovery of recyclable materials.
These measures promote a more sustainable and eco-friendly approach to waste management.
To summarize, AI is pivotal in achieving both economical and environmental sustainability in waste management.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of AI in Waste Management
Several cities and regions have successfully implemented AI-powered smart waste management systems. These case studies showcase the tangible benefits and demonstrate the potential for widespread adoption of these technologies.
Examining these success stories provides valuable insights into how AI can be effectively integrated into existing waste management infrastructures.
City of Copenhagen, Denmark
Copenhagen uses AI to optimize waste collection routes, resulting in:
- A 20% reduction in fuel consumption for collection vehicles.
- A 15% decrease in greenhouse gas emissions.
- Improved air quality due to fewer vehicles on the road.
This initiative has significantly contributed to Copenhagen’s sustainability goals.
AMP Robotics, USA
AMP Robotics develops AI-powered sorting systems that:
- Increase recycling rates by up to 50%.
- Reduce contamination of recyclable materials.
- Lower the cost of recycling operations.
Their technology has been adopted by numerous recycling facilities across the United States.
These examples prove that investing in and implementing AI technologies enhances waste management practices.
Challenges and Considerations
While AI offers tremendous potential for improving waste management, there are challenges and considerations that need to be addressed. Overcoming these obstacles is crucial for the successful and sustainable implementation of smart waste management systems.
Understanding these challenges will help stakeholders make informed decisions and mitigate potential risks.
Initial Investment Costs
Implementing AI-powered systems often requires significant upfront investment in:
- Hardware: installing sensors, cameras, and robotic arms.
- Software: developing and deploying AI algorithms.
- Training: educating staff on how to operate and maintain the new systems.
However, these costs can be offset by long-term savings and increased efficiency.
Data Privacy and Security
The use of AI in waste management involves collecting and analyzing large amounts of data, raising concerns about:
- Data privacy: protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Data security: preventing cyberattacks and data breaches.
- Ethical use: ensuring data is used responsibly and transparently.
Robust data protection measures are essential to maintain public trust.
To conclude, responsible implementation of AI technologies is important.
The Future of Smart Waste Management
The future of smart waste management looks promising, with ongoing advancements in AI and related technologies. As AI continues to evolve, its role in waste management is expected to expand, driving further improvements in efficiency, sustainability, and resource recovery.
Embracing these innovations is crucial for creating cleaner, more resilient cities.
Emerging Technologies
Several emerging technologies are poised to further enhance AI-powered waste management, including:
- IoT sensors: providing real-time data on waste levels and composition.
- Blockchain: ensuring transparency and traceability in the waste supply chain.
- Additive manufacturing: using recycled materials to create new products.
These technologies will work synergistically to create a circular economy.
Policy and Regulation
Supportive policies and regulations are essential to encourage the adoption of AI in waste management, such as:
- Incentives: offering tax breaks and subsidies for implementing AI solutions.
- Standards: establishing clear guidelines for data privacy and security.
- Public awareness: promoting the benefits of smart waste management.
These measures will create a favorable environment for innovation and investment.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| ♻️ AI Sorting | AI-powered robots improve sorting accuracy and speed. |
| 🚚 Route Optimization | AI optimizes waste collection routes, reducing fuel consumption. |
| 💰 Cost Savings | AI cuts labor and fuel costs while boosting recycling revenue. |
| 🌱 Environmental Impact | AI minimizes methane emissions and leachate contamination. |
Frequently Asked Questions
▼
AI enhances waste sorting through computer vision and robotic arms, identifying and separating recyclable materials with greater precision and speed, reducing contamination.
▼
Optimized collection routes, powered by AI, reduce fuel consumption, lower emissions, and minimize travel time by analyzing real-time traffic and waste fill levels.
▼
AI solutions cut waste management costs by automating sorting, optimizing collection, reducing labor needs, and increasing revenue from recycled materials.
▼
AI reduces methane emissions, minimizes leachate contamination, and conserves natural resources by improving recycling rates and diverting waste from landfills.
▼
Key challenges include high initial investment costs, data privacy and security concerns, and ensuring responsible and transparent use of data in waste management processes.
Conclusion
Embracing smart waste management through AI-powered systems is essential for reducing landfill waste, improving operational efficiency, and creating more sustainable cities. By addressing the challenges and leveraging emerging technologies, communities can pave the way for a cleaner, more resilient future.